Temporal Segment Networks for Action Recognition in Videos
#Temporal Segment Networks for Action Recognition in Videos
这篇是最近研究的论文的起始论文,提出了一种基于分片采样的策略,传统的不论是双流法还是三维卷积法,受限于 GPU 资源和网络结构的限制,都只能处理一段时间内的视频帧,没有办法做到长时间的采样。
As discussed in Sec. 1, long-range temporal modeling is important for action understanding in videos. The existing deep architectures such as two-stream ConvNets [1] and 3D convolutional networks [16] are designed to operate on a single frame or a stack of frames (e.g., 16 frames) with limited temporal durations. Therefore, these structures lack capacity of incorporating long-range temporal information of videos into the learning of action models.
要解决这样一个问题,有两种方向,第一种是stacking more consecutive frames,第二种是sampling more frames at a fixed rate,即要么堆叠更多的帧数,要么进行局部采样。
但是前者会造成计算复杂度急剧升高,后者会导致模型不能很好地表达完整的信息。
与此同时,作者注意到,其实连续的多帧中其实内容变换很少,所以提出了一种segment based sampling的采样策略。
although the frames are densely recorded in the videos, the content changes relatively slowly.
这个策略的思想其实还蛮简单的,看图就懂了:
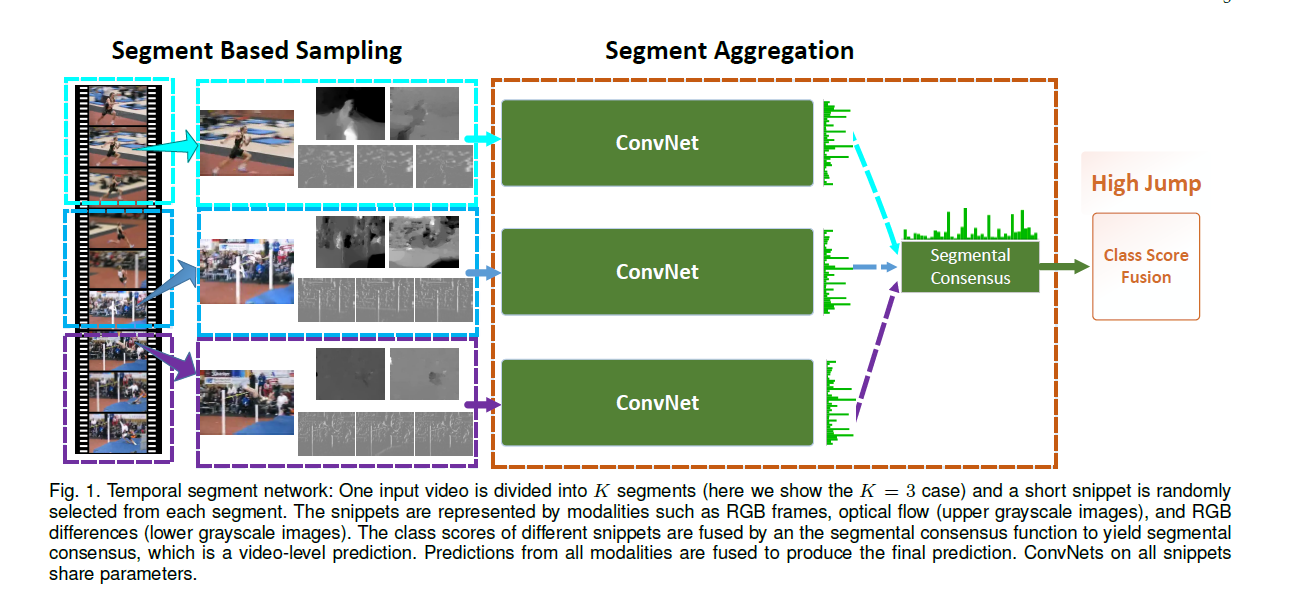
本质上就是先把视频均分成等份,然后每一份里选取一个RGB、Optical Flow或RGB Differences之类的来代表这一个片段的信息,然后提取这一片的信息(CNN)进行信息融合。
#融合函数
所以整个网络其实就是有三段:分段特征表示、分段信息提取和多段信息融合。
现在往回看去,分段特征表示就是将多帧图像的信息进行转化,转化成一个可以用来计算的方法,即前面所说的RGB、Optical Flow或RGB Differences。
分段信息提取是属于骨干网络的事情,我们也无法进行修改。
故最重要的部分就是,如果将多个分段所提取到的信息进行融合,这个对于模型的表达能力来说,是十分重要的。
As analyzed above, the consensus (aggregation) function is an important component in our temporal segment network framework.
论文中给出了五种融合方法:max pooling、average pooling、top-K pooling、weighted average、attention weighting。
前两个就不解释了,第三个相当于不取最大的,而是取最大的K个进行平均,k=1即max pooling,k=[分片数]即average pooling。
第四个和第五个相当于在平均池化的基础上给每个分片进行了加权。
(PAN 的创新之一就是提出了一种新的加权方式)